-

A Research on Colours and Fastness Values of Different Materials Dyed with Some Natural Dyes
Selma Dolanbay Doğan,
Meral Akan
Issue:
Volume 7, Issue 3, May 2018
Pages:
69-74
Received:
12 February 2018
Accepted:
13 March 2018
Published:
4 April 2018
Abstract: Nowadays use of natural materials and natural methods is considered to be an element that increases the value of a product and contributes to sustainable life in environmental, economic and sociologic senses. Natural dyeing has been an avocation performed in the Anatolia region for centuries and can be used for dyeing of different materials. In this study, it is aimed to expose color values, color named, light and rubbing fastness of the colors that were obtained as a result of dyeing three different materials (wool yarn, cotton fabric and paper) with some natural dyes according to traditional method. In line with this aim, the materials were dyed with madder (Rubia tinctorium L.), walnut (Juglans regia L. ), weld (Reseda luteola) and indigo. In consequence of the research; color names, color values, light and rubbing fastness of fifteen samples were determined. The result of the research were evaluated statistically using SPSS programme.
Abstract: Nowadays use of natural materials and natural methods is considered to be an element that increases the value of a product and contributes to sustainable life in environmental, economic and sociologic senses. Natural dyeing has been an avocation performed in the Anatolia region for centuries and can be used for dyeing of different materials. In thi...
Show More
-

Analysis of the Interaction of NH4Cl-Doped Process Gases with Zinc-Coated Surfaces with Regard to Aluminum Brazing with Zn-AlSi Duplex Braze Metal Coatings
André Langohr,
Sarah Groß-Bölting,
Ulrich Holländer,
Kai Möhwald
Issue:
Volume 7, Issue 3, May 2018
Pages:
75-84
Received:
14 December 2017
Accepted:
26 January 2018
Published:
23 April 2018
Abstract: This paper reports on the development of a braze metal coating and a brazing process for joining aluminum alloys at temperatures < 570°C without applying a flux before brazing. This is achieved using a duplex braze metal coating made of an aluminum-silicon alloy and zinc as top layer in combination with the use of hydrogen chloride doped nitrogen as process gas. Here hydrogen chloride deoxidate the surface of the zinc coating and form zinc chloride flux in-situ. Defined hydrogen chloride partial pressures between 100 vpm (volume parts per million) and 300 vpm in nitrogen were produced by thermal decomposition of solid ammonium chloride. Reaction kinetics of hydrogen chloride with the zinc coating was investigated by detecting the generation of reaction heat at different hydrogen chloride concentrations and temperatures. An activation energy of
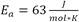
was determined, a value that matches the values stated in the literature. The order of reaction n was found to be significantly lower than 1, which is consistent with gas solid reactions at microscopically fissured interfaces. An in-situ zinc chloride formation rate of 3 µg/(min cm
2) at 400°C and 200 vpm hydrogen chloride concentration was obtained from the measured data, which may be sufficient for triggering the flow of braze metal. Experimental brazing tests showed, that when the reaction time was long enough to permit the formation of zinc chloride and this is followed than by a brazing process at 560°C to 570°C in subsequently hydrogen chloride-free nitrogen atmosphere, a liquid ternary AlSiZn braze metal is formed from the dublex coating enabling a wetting and brazing of the contacting join partner.
-

The Effects of Ozone Bleaching and Ozone Desizing Method on Whiteness and Water Absorption of 100% Cotton Terry Fabrics
Yıldıray Turhan,
Şeyma Soydaş
Issue:
Volume 7, Issue 3, May 2018
Pages:
85-94
Received:
11 March 2018
Accepted:
27 March 2018
Published:
24 April 2018
Abstract: In this study, the effects of ozone desizing and bleaching on the hydrophilicity and whiteness of terry fabrics were investigated. The results were compared with those obtained after conventional desizing and bleaching (hydrogen peroxide bleaching). The test samples contain two side piled woven terry cloths of four different areal weights. The ozone desizing and bleaching process was carried out at fixed PH values (6) in four different ozonation times and two different ozone doses. The rate of water pickup in fabrics was 60%. It has been determined that as ozonation time and the ozone dose increase, the degree of whiteness and water absorption of the terry fabric increases. However, the increase in the ozonation time did not cause a significant change in the low ozone doses; the change in the ozonation time at high ozone doses is causing a marked change in the investigated properties of the towel fabric. The degree of hydrophilicity and whiteness achieved after ozonation was found to be close to the results obtained in conventional bleaching. However it was seen that although acceptable water absorbency was obtained by the ozone desizing method, these values were lower than those of the conventional desizing method. Ozone bleaching and desizing do not require the consumption of water, the consumption of heat energy, and the use of any chemical additive that harms the environment with its wastes. As a result, owing to ecofriendly, saving energy and acceptable fabric properties with regard to whiteness and absorptivity, ozone bleaching can be applied instead of the conventional bleaching and desizing method.
Abstract: In this study, the effects of ozone desizing and bleaching on the hydrophilicity and whiteness of terry fabrics were investigated. The results were compared with those obtained after conventional desizing and bleaching (hydrogen peroxide bleaching). The test samples contain two side piled woven terry cloths of four different areal weights. The ozon...
Show More
-

Selective Separation of Organic Electrolytes by Neutralization Dialysis with Grafted Polyethylene Films
Yuji Kimura,
Kazunori Yamada
Issue:
Volume 7, Issue 3, May 2018
Pages:
95-105
Received:
14 November 2017
Accepted:
30 November 2017
Published:
26 April 2018
Abstract: The selective separation of organic electrolytes by neutralization dialysis was investigated with two kinds of grafted polyethylene (PE) films prepared through the photografting of 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) onto the PE films and the subsequent quaternization and through the photografting of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and the subsequent sulfonation. The permeation flux of benzoic acid (BA) for the quarternized DMAEMA-grafted PE (PE-g-QPDMAEMA) films increased with an increase in the degree of quaternization, and the BA permeability had the maximum at the initial pH value of the permeate solution of 12.0. On the other hand, the sulfonation offered the phenylalaninol (Phl) permeability of the GMA-grafted PE (PE-g-PGMA) films. The selective separation for the binary BA/Phl or 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid/Phl systems was successfully achieved by use of a pH difference between the feed and permeate solutions through the PE-g-QPDMAEMA and sulfonated PE-g-PGMA (PE-g-SPGMA) films. The maximum selective separation was obtained under the conditions that the initial pH values of the permeate solutions through the PE-g-QPDMAEMA and PE-g-SPGMA films were adjusted to 12.0 and 2.0, respectively. This procedure will be applied to separation and concentration of organic electrolytes and water purification.
Abstract: The selective separation of organic electrolytes by neutralization dialysis was investigated with two kinds of grafted polyethylene (PE) films prepared through the photografting of 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) onto the PE films and the subsequent quaternization and through the photografting of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and the su...
Show More
-

Evaluation of Sample-Electrode Contact Impedance in Two-Point Measured AC Impedance Spectroscopy of Cement-Based Materials
Fuqiang He,
Ruipan Wang,
Runxiao Zhang,
Changping Chen,
Li Lin,
Xiaopeng An
Issue:
Volume 7, Issue 3, May 2018
Pages:
106-114
Received:
11 March 2018
Accepted:
24 April 2018
Published:
22 May 2018
Abstract: In this study, AC impedance spectroscopy measurements of cement paste with 0.5 W/C were collected and interpreted using different electrode-sample contact methods. The results indicated that when using a conductive glue contact (CG), two capacitive loops and an inclined line appeared within the frequency range of 100-0.1 Hz. An equivalent circuit, Rs (Cd1 (RctZw)) (Rd2Cd2), was proposed for contact impedance of the electrode-sample interface, and correction of error caused by the contact impedance of electrode-sample indicated that the contact impedance had almost no effect on the ACIS measurements of the cement paste with CG contact in the present curing conditions. When the samples were cured in a fog room, the CG and electrode pre-casting (EP) contact had similar interpreted parameters (Pcp). However, the demolded sample-electrode (DS) contact method and the drying environment used in the manufacture of the EP contact can significantly change Pcp. In this situation, both of CG and EP contact are reasonable for ACIS measurements of cement-based materials. EP contact cannot be used for samples cured in a drying environment, and DS contact cannot be recommended for ACIS measurements of cement-based materials.
Abstract: In this study, AC impedance spectroscopy measurements of cement paste with 0.5 W/C were collected and interpreted using different electrode-sample contact methods. The results indicated that when using a conductive glue contact (CG), two capacitive loops and an inclined line appeared within the frequency range of 100-0.1 Hz. An equivalent circuit, ...
Show More




